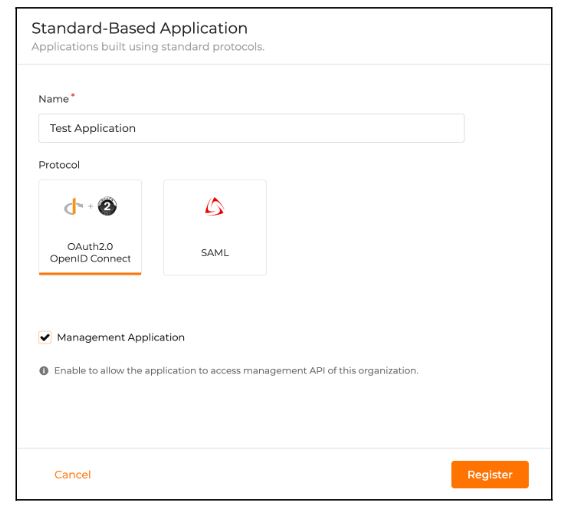
How to Manage Your Device Fleet in the Age of IIoT
Main drivers of an IIoT ecosystem, device management strategies, and getting started.

Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) today
The internet has grown to remarkable eminence, progressing a long way from its humble beginnings as a coke vending machine1 following basic instructions. Today, the semantic web engages with us interactively and processes information for us intelligently.
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses a connected system of devices and sensors with the ability to gather, process, and exchange data over a network (not necessarily the internet), thereby enabling remote monitoring, evaluation, and administration of such devices. In a broader sense, this is about the integration of people, processes, and technology with devices, harnessing the best of each and making our lives easier.
With the advent of Industry 4.0, we are thrust forward with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). It is a common misconception to think of IIoT as an extension of IoT. In reality, however, it is just a subcategory of IoT that expands into industrial applications of IoT. IIoT has evolved from Distributed Control Systems (DCS), where autonomous controllers were distributed throughout a system with localized control. Today, it is directed towards automation and improving the operational efficiencies of large industrial processes. It also includes consumer-facing applications such as wearable devices, smart home technologies, and self-driving cars.
In essence, both IoT and IIoT consist of a system of connected devices, machines, sensors, and infrastructure that transmits data via a network with the ability to remotely administer devices and processes.
IIoT is the decisive factor that empowers the Fourth Industrial Revolution, smartly dubbed Industry 4.0. Enabled by powerful emerging technologies such as Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), advanced robotics, big data, edge computing, and other innovative breakthroughs, IIoT is becoming an inescapable big player in our lives.
IIoT technologies empowering Industry 4.0
Having leapfrogged from steam engines2 to supercomputers by the Third Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0 explores closer integration of digital technologies with the physical world in various industries to enhance efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
Energy conserving smart cities with optimally controlled traffic, smart factories with digital twins maneuvering laborious tasks, and collaborative robots (Cobots) working alongside human operators are only some items on the IIoT promise shelf. Insights derived from wide data sources and analytics, predictive maintenance capabilities, and progressive automation are other transformative changes brought about by leveraging the power of connected devices and data analytics, leading to heightened competitiveness and sustainable growth in industries.
The technologies enabling and empowering IIoT vary from cybersecurity, cloud computing, edge computing, machine-to-machine communication, 3D printing, extended reality (XR), advanced robotics, big data, radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, cognitive computing, and a multitude of other such advancements in different fields.
Among them, some are more potent drivers that distinctively characterize an IIoT ecosystem. These include:
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS): As the term implies, these systems are composed of digital systems integrated into the physical processes of an industry. Cyber-physical systems play a pivotal role in Industry 4.0 by connecting the physical and digital realms to enable more accurate decision-making, automation, optimization, and enhanced collaboration between humans, machines, and processes. They are a fundamental component of the smart, interconnected ecosystems that characterize Industry 4.0.
- Cloud computing: A novel concept of getting the required computing services for a specified period of time over the internet instead of provisioning local hardware and infrastructure. Cloud computing covers a wide range of services, including storage, processing power, networking, and software. It offers various service models, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), catering to different levels of control and management. The elasticity of cloud computing, i.e., the ability to scale up or down as per changing workloads, ensures improved performance and efficient use of resources. Because cloud computing is a measured and on-demand service, it ensures cost-effective resource consumption and commercial viability.
- Edge computing: This is a decentralized computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where they are needed instead of remotely accessing them via cloud servers. Data processing occurs at or near the “edge” of the network, typically closer to the source of data generation, which could be sensors, devices, machines, or users. Edge computing delivers reduced latency, real-time responsiveness, enhanced security, and improved bandwidth efficiency. It’s a critical technology for applications that require rapid processing and decision-making, especially in IIoT applications and Industry 4.0.
- Big data: Comprises the massive volume of structured and unstructured data generated from various sources at a high velocity. This data is often too complex and large to be effectively processed and analyzed using traditional database management tools and methods. Big data encompasses a wide range of data types: text, images, videos, sensor readings, social media interactions, and more.
- AI and ML: These technologies are critical requirements to transform raw data into insights that drive operational performance in industrial processes. They facilitate real-time data and updates, enhance operations, and enable predictive capabilities.
AI and ML algorithms expedite data analysis and pattern recognition by processing large volumes of IIoT-generated data that help with predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and real-time decision-making. Cognitive computing enables IIoT systems to understand and respond to natural language queries and instructions, thereby simplifying user interaction with complex industrial systems.
IIoT device management strategies
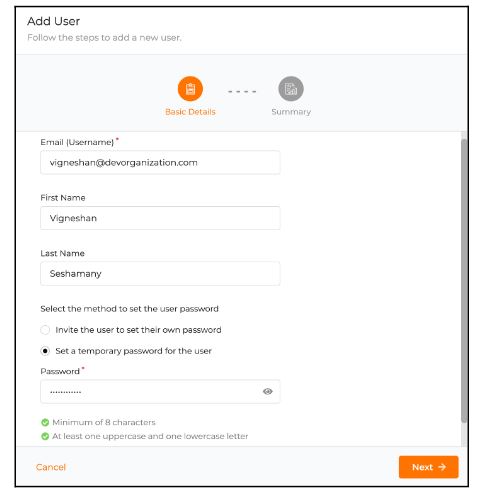
With Industrial IoT, we are talking about many different types of devices connected and integrated into a single digital ecosystem that seamlessly operate with each other and run multiple business processes efficiently. It is therefore imperative to have an effective device management strategy for your enterprise to ensure the security, robustness, and efficiency of your system. As an ever-increasing number of industrial devices become connected and integrated into the digital ecosystem, effective management and administration become a tedious task demanding much attention, time, and resources. Not so, however, if you have done your homework beforehand.
It is important to be aware of and proactively address the potential challenges of handling a collection of devices out at large. Some of the key factors to consider when managing fleets of disparate devices are displayed below.
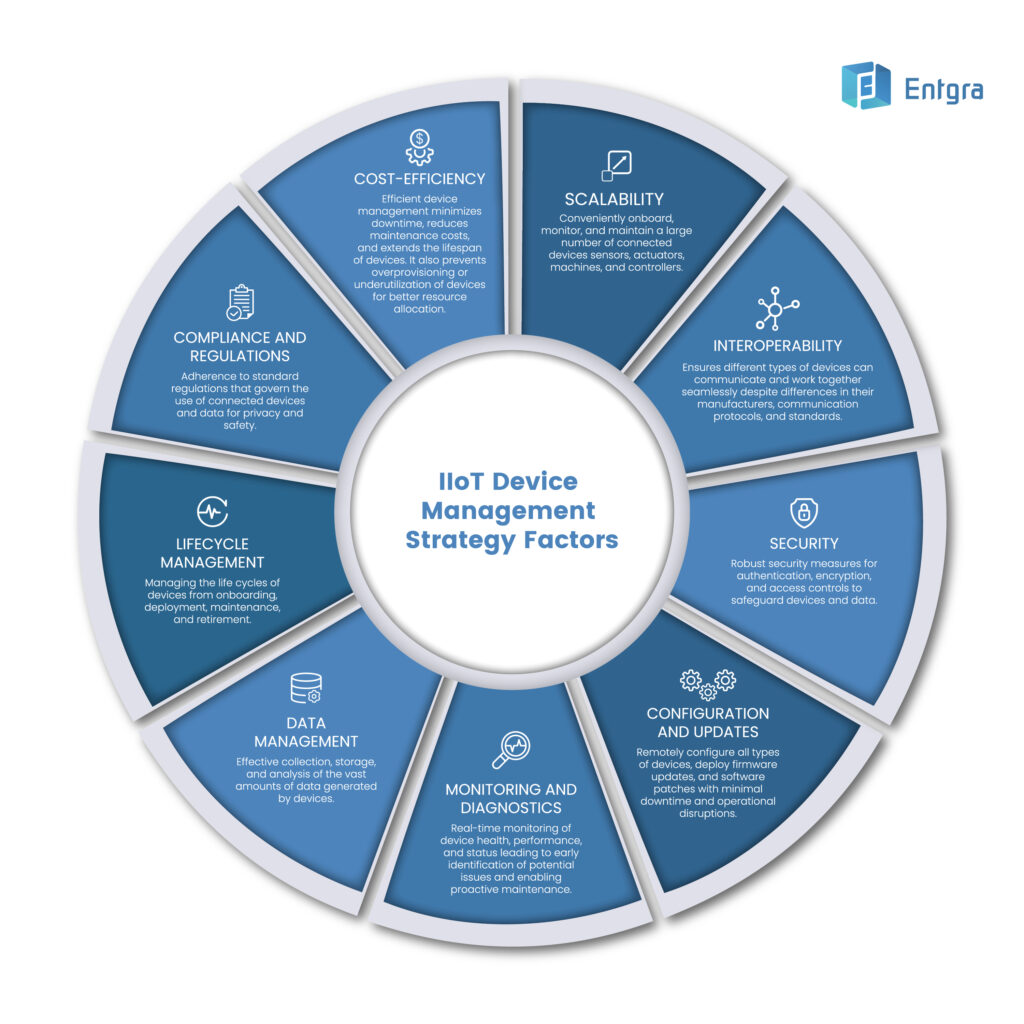
Illustration: Device management strategy factors to consider when managing large device fleets
Securing your edge with Entgra solutions
Imagine having to herd a fleet of devices – hundreds and thousands of them at that – concurrently, efficiently, and flawlessly around the clock on multiple platforms, each with its own configuration settings and running on different operating systems? Quite the nightmare for a modern IT-admin shepherd if not for the convenience of effective device governance strategies at our disposal today.
Endpoint devices encompass physical equipment connected to the digital ecosystem, exchanging with and sometimes processing information for the network. These include the commonly identified mobile devices, embedded devices, desktop computers, kiosks, virtual machines, servers, and wearables, as well as facilitating devices like routers, network gateways, firewalls, and load balancers. Each of these comes with its own manufacturer and is often run on specific operating systems such as iOS, Android, or Windows. They gather, exchange, and sometimes process data which needs to be utilized securely and translated into intelligible information. This process is often handled by single-console device control and administration. Privacy regulations, device policies, and other factors that must guarantee the security of devices and data are also integral components of the process.
What the shepherd needs today, then, is a crook that can enroll, administer, and manage the whole of the device fleet with zero-touch (literally) agility and enable ceaseless, robust operation of the process with minimal intervention.
Entgra UEM for centralized device management and unified endpoint management (UEM) has extensive enterprise-wide customizable UEM features offering granular, simplified experiences and robust identity management capabilities. With its ability to trigger operations simultaneously in a device group, live feed, and Grafana-based dashboards, an IT administrator’s life is simplified manyfold.
The Entgra IoT Platform facilitates end-to-end IoT application development on one platform, giving you the ability to integrate all your devices and solutions.
Device location tracking, enterprise wipe, device lock, and restriction policies are some of the security features Entgra offers as an accredited Google Enterprise EMM Partner for Android devices.
Presently, our industry solutions cover factory floor monitoring, kiosk management, and utility meter connectivity. We provide customized IoT solutions catered to your specific factory floor device monitoring and control requirements and scalable kiosk management propositions befitting long-term growth.
Entgra solutions combined would just be the shepherd’s crook that your enterprise needs to flourish unrestrained.
Get onboard with our Try-It-Now product packages or contact us for further information on how we can help you.
References
1. The first device on the Internet of Things – the first ARPANET-connected appliance – was a modified Coca-Cola vending machine at Carnegie Mellon University in 1982, marking the beginning of a network of smart devices. The machine was able to report its inventory and whether newly loaded drinks were cold.
2. Each Industrial Revolution has been marked by distinctive economic, social, and cultural changes. The First Industrial Revolution saw the transition from hand production methods to machines through the use of steam and water power.