Easier device enrollment with Windows Autopilot, real-time issue resolution, and policy support for better control of Android devices with Entgra UEM 6.1
Entgra UEM 6.1, the successor to Entgra UEM 6.0, is now available for use.
The latest version of our unified endpoint management (UEM) product has several benefits for Windows and Android device users. Windows device users will benefit from streamlined device setup through Autopilot enrollment and faster real-time technical support with remote screen share. This release also introduces new device operations to enhance management capabilities. Android device users can now enforce pre-approved input methods for better management of data usage. Entgra UEM 6.1 comes with UI enhancements that give you improved navigation and usability, while platform improvements include convenient tenant deletion.
This blog explores each of these new benefits by device type in detail and other platform improvements.
For Windows Device Users
Simpler Device Setup with Windows Autopilot Enrollment
Use Windows Autopilot deployment for a straightforward, hassle-free device setup and configuration for your corporate Windows devices. This feature provides:
- Zero Touch Deployment: Autopilot supports zero-touch deployment scenarios, where you can provision and configure devices remotely sans any physical interaction. This is especially useful for large-scale remote workforces.
- One-time setup: Autopilot eliminates the need for repetitive manual deployment tasks, such as device activation, user account creation, and app deployment. This one-time setup streamlines the process and saves significant time for your administrators.
- No OS imaging required: With Autopilot enrollment, you can effortlessly distribute applications, documents, and configurations to enrolled devices in bulk. This gives you a simplified deployment process by shortening the time-consuming OS imaging process.
- Controlled Administrative Permissions: Autopilot helps enforce security policies by limiting the creation of local administrator accounts on devices. This ensures that only authorized personnel can control administrative permissions across your devices.
- Less TCO: By streamlining the deployment and management process, Autopilot can help reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) associated with managing Windows devices. This is often achieved by minimizing the time and resources required for manual setup and configuration, thus leading to cost savings in the long run.
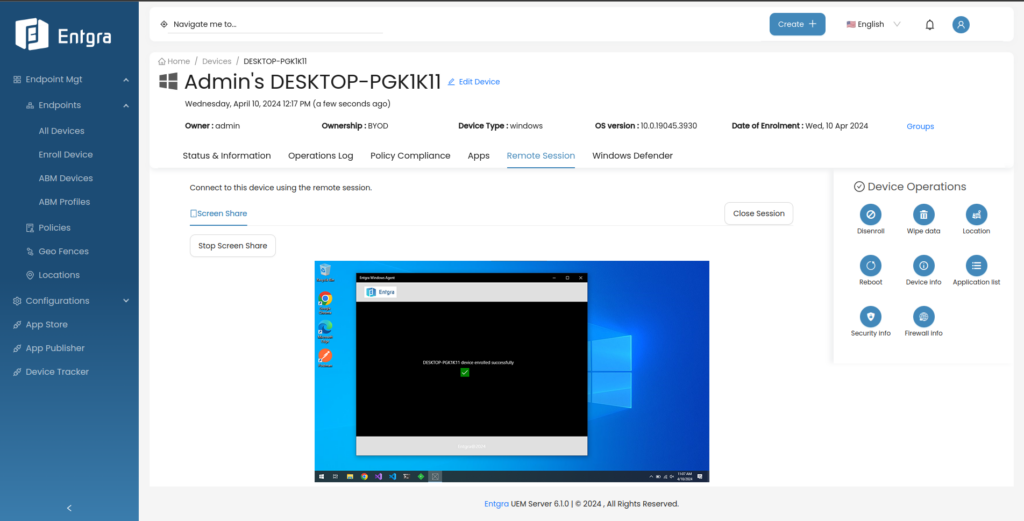
Interactive Real-Time Technical Support Facilitated by Remote Screen Share
The new remote screen share support feature empowers your IT admins to promptly identify and resolve issues directly by viewing your users’ screens in real-time.
This feature has a significant impact on your troubleshooting process and improves the overall efficiency of your support operations. With instant visual inspection and diagnosis, your IT teams can expedite solutions, enabling employees to resume their tasks quickly and reduce instances of downtime. There are further cost saving benefits for your business as your team does not have to make on-site visits for technical issue resolution unless absolutely necessary.
We have plans to develop our real-time technical support feature further in upcoming product releases.
Tailored Device Management Through Device Operation Enhancements
This release expands on our existing suite of remote operations available for Windows device users. The additions are discussed further below.
- Device Info: You can request detailed device information directly from enrolled Windows devices. This includes crucial data such as hardware specifications, system configurations, and more, enabling administrators to gain deeper insights into their device ecosystem to support management and decision-making.
- Application List: Gain up-to-date information about your software landscape across your Windows devices with the “Application List” functionality. Triggering this operation allows you to download the Microsoft Application list from enrolled devices, providing visibility into installed applications and their versions.
- Security Info: With the “Security Info” feature, you can request comprehensive security information from enrolled Windows devices. This includes vital data regarding device security settings, defender details, encryption status, and more, empowering administrators to ensure compliance with security policies and proactively address any vulnerabilities.
- Firewall Info: Gain deeper visibility into the network security posture of Windows devices with the “Firewall Info” functionality. By triggering this operation, administrators can request device firewall information from enrolled Windows devices. Use this data for better network security management, threat detection, and response capabilities.
For Android Device Users
Updated Data Security With Pre-Approved Input Methods
Android device users can now regulate the use of keyboards and input methods, reducing the occurrences of data breaches and keylogging incidents.
This feature presents you with various options to customize input methods so that you have the flexibility to adapt the policy based on your enterprise needs. You have the choice to either restrict input methods solely to trusted pre-installed or system-provided keyboards, ensuring a heightened level of security, or alternatively, define a specific list of user-installed packages deemed acceptable as input methods.
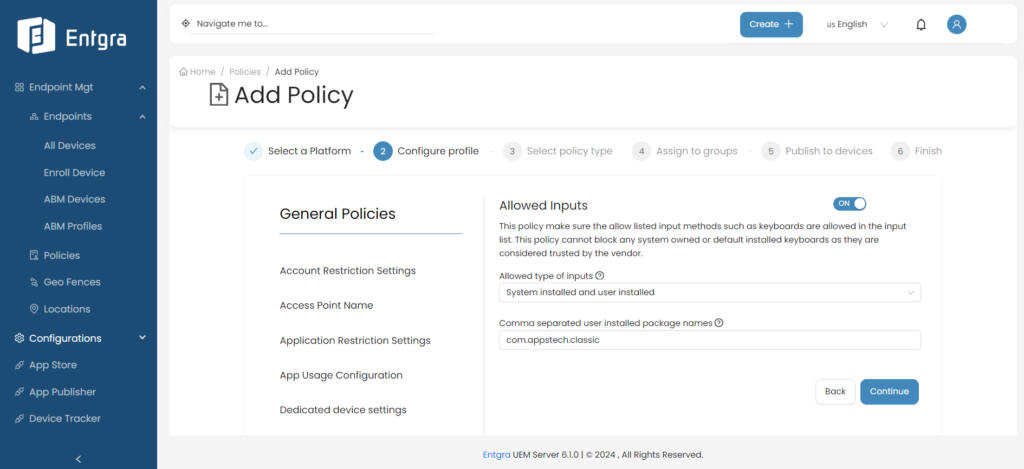
This level of granularity empowers you to fine-tune your device management strategy, enhancing security while maintaining operational flexibility.
Block Apps From Using Metered Connection With Improved App Usage Configuration
The improved App Usage Configuration policy gives you the ability to restrict specific applications from accessing the internet when your device is connected to a network with metered or limited data usage, such as cellular data networks.
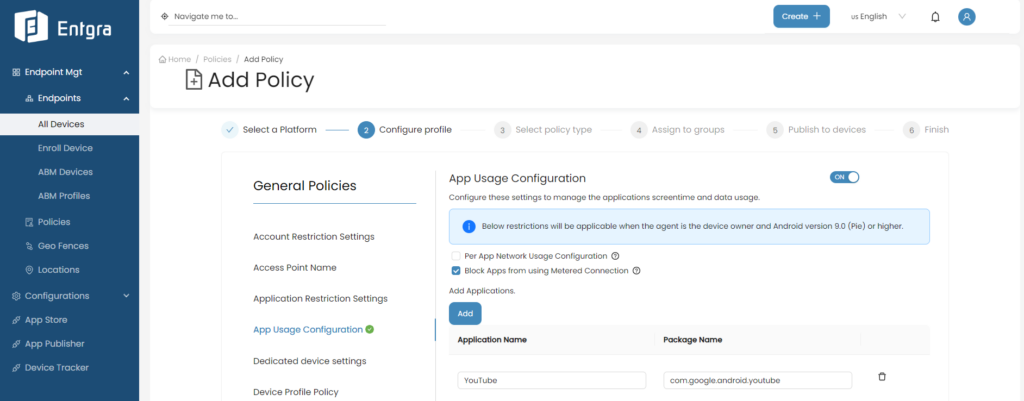
Manage your data usage more effectively, avoid unexpected overage charges, and save financial resources with this feature. You can also ensure that essential apps or services take priority.
Agent Compatibility for Android 14 and 13
Entgra UEM 6.1 provides comprehensive compatibility with Android versions 14 and 13 for its agent. This ensures a smooth integration of diverse device fleets, offering enhanced management capabilities across a range of Android devices.
Platform and UI Improvements For All Devices
Faster Tenant Deletion
Admins have an advanced feature to efficiently manage subtenants and their data, all accessible within a single console interface. Deleting tenants and clearing relevant data becomes less time-consuming because you do not have to switch between multiple consoles. Furthermore, admins can still maintain control over your multi-tenant environments.
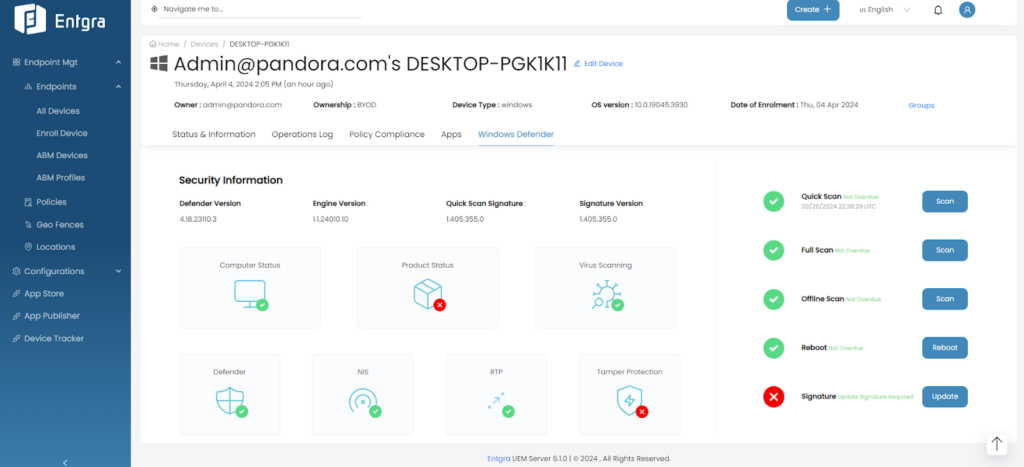
Revamped Windows Defender Page and Enhanced Search Functionality
Continuing our mission to keep improving our product user interface and give administrators a smoother navigation experience, Entgra UEM 6.1 introduces features to this end. You can now conveniently search for apps using package names within the application restriction policy, easing app management tasks.
Furthermore, enhancements to the Windows Defender single-device page provide a more intuitive user experience.
Experiment with these features by signing up for your 14-day free trial today or reach out to us for a live demo. Our product documentation has more details to help you get started too. Stay connected with us to learn about future product updates to Entgra UEM.